Point of Care Ultrasound for Paramedics and Nurses
POCUSSTUFF
Imaging Windows
Each patient’s anatomy and body habitus is slightly different from one another. So, for all images acquired; depth, gain/TGC, and probe orientation must be adjusted in order to optimize the images obtained
Lung
Probe/Preset:
Linear, Phased Array / Lung, FAST, Cardiac, Pediatric Lung
Body Plane:
Sagittal
Probe Indicator:
Towards Head
Depth:
-
6cm to Evaluate for Lung sliding
-
>16cm for Evaluation of Lung Pathology
Location:
-
Anterior: 2nd to 3rd Intercostal Space, Midclavicular Line
-
Lateral 4th to 5th Intercostal Space, Mid to Posterior Axillary Line
Identify:
-
Lung Sliding
-
Horizontal uniformly repeating A-Line reverberations
-
Vertical B-line "comet-tails" that originate at the pleural line and extend to the deep field of the image.
Notes:
Slide Probe downwards towards the feet evaluating for lung sliding in multiple rib spaces. May also consider scanning along the midaxillary line. A shallow scan will optimize visualization of lung sliding. A deeper scan is required to evaluate for B-lines and other pathology. 2 or less B-lines per rib space is considered normal.
_edited.jpg)



Parasternal Long Axis
(PLAX)
Probe/Preset:
Phased Array / Cardiac
Body Plane:
Relative to the heart
Probe Indicator:
Towards Patient’s Right Shoulder
Depth:
At least 15cm
Location:
Left Sternal border, 3rd to 5th Intercostal Space. Similar location to V2
Identify:
-
Left Ventricle
-
Right Ventricle
-
Intraventricular Septum
-
Mitral Valve
-
Aortic Valve
-
Descending Aorta
Notes:
Assess for cardiac motion and the presents of a large pericardial effusion. Multiple views should be acquired to confirm the presents of a pericardial effusion. Global Cardiac function can be visually assessed or measured using M-Mode by evaluating E-Point Septal Separation (EPSS).

_edited.jpg)
_edited.jpg)
_edited.jpg)

Parasternal Short Axis
(PSAX)
Probe/Preset:
Phased Array / Cardiac
Body Plane:
Relative to heart
Probe Indicator:
Towards Patient’s Left Shoulder
Depth:
At least 15cm
Location:
Left Sternal border, 3rd to 5th intercostal space. Similar location to V2
Identify:
-
Left Ventricle
-
Right Ventricle
-
Mitral Valve
-
Papillary Muscles
Notes:
From the optimal PLAX view rotate the probe 90* right, towards the left shoulder, to obtain the PSAX view. By fanning the probe right and left you are able to evaluate the heart through multiple levels. (ex: Mitral Valve, Mid-Ventricular, Basal Left Ventricular Segments)
_edited.jpg)




Apical Four Chamber
(A4C)
Probe/Preset:
Phased Array / Cardiac
Body Plane:
Relative to the heart
Probe Indicator:
Towards Patient’s left
Depth:
At least 20cm
Location:
Point of Maximal impulse, approximately the 5th intercostal Space, midclavicular line, with probe pointed face pointed towards the right scapula Similar location to V4 or V5
Identify:
-
Left Ventricle
-
Right Ventricle
-
Left Atria
-
Right Atria
-
Mitral Valve
-
Tricuspid Valve
Notes:
For the optimal A4C view the intraventricular septum should be roughly vertical on the screen. This is a good view to evaluate relative chamber size. Ensure proper probe orientation during scan, otherwise right and left sides of the heart may be misidentified.

_edited.jpg)



Subcostal Four Chamber
(S4C)
Probe/Preset:
Curvilinear, Phased Array / FAST, Cardiac
Body Plane:
Relative to the Heart
Probe Indicator:
Towards Patient’s Left
Depth:
At least 20cm
Location:
Patient Midline, in the epigastric to subxiphoid space. Approximate 15-20* angle of the probe relative to the patient's skin surface, with probe face angled towards the head
Identify:
-
Liver
-
Left Ventricle
-
Right Ventricle
-
Mitral Valve
-
Tricuspid Valve
Notes:
Good for pericardial effusions, and cardiac activity intra-arrest. This view maybe difficulty to obtain due to patient anatomy. Utilize the liver as an acoustic window to visualize the heart. Adjust gain and depth to optimize image.
_edited.jpg)



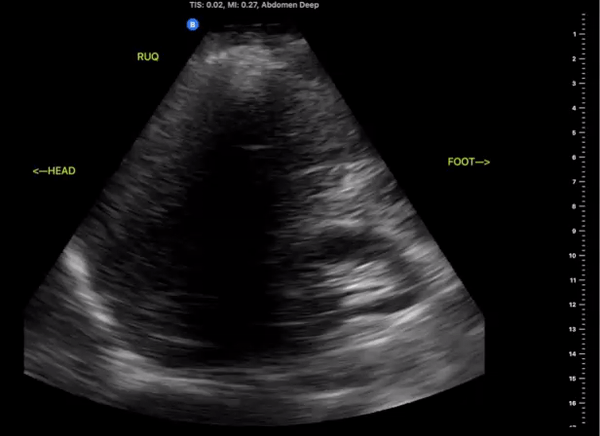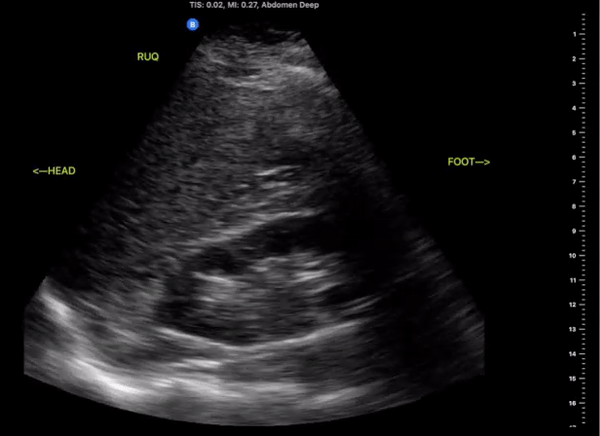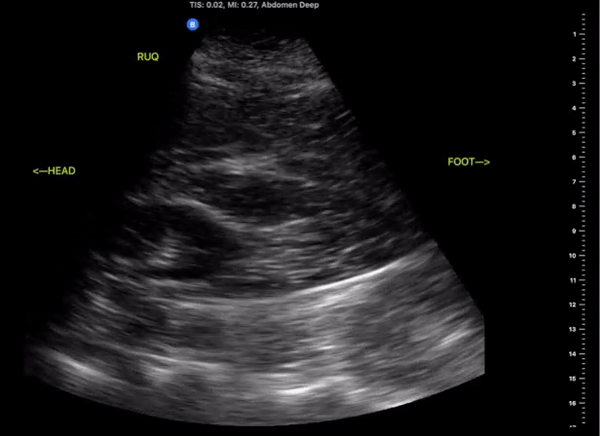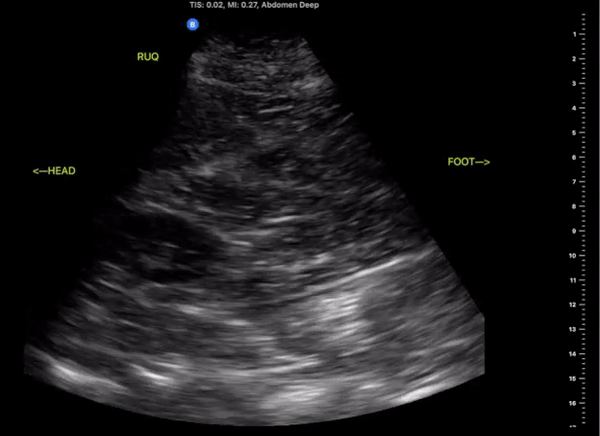
Right Upper Quadrant
(RUQ)
Probe/Preset:
Curvilinear, Phased Array/ FAST, Abdominal
Body Plane:
Coronal
Probe Indicator:
Towards Head
Depth:
At least 15cm
Location:
Mid axillary to anterior axillary line at the level of the xiphoid scanning posteriorly
Identify:
-
Right kidney
-
Liver
-
Diaphragm
-
Spinal Stripe
Notes:
The scan of the RUQ should be dynamic, starting at the interface between the lungs, diaphragm, and liver. Slide the probe towards the feet capturing views Morrison’s Pouch, inferior pole of the kidney and right Pericolic Gutter


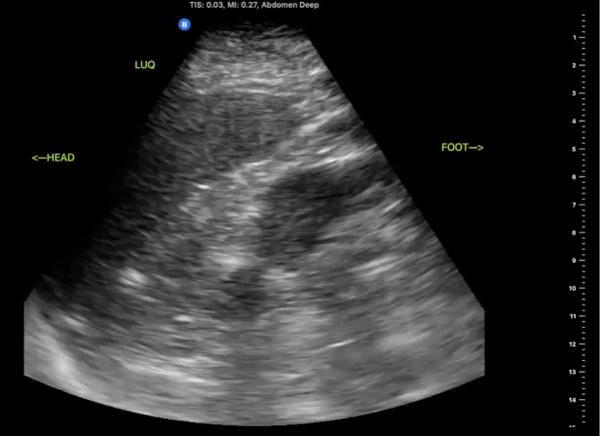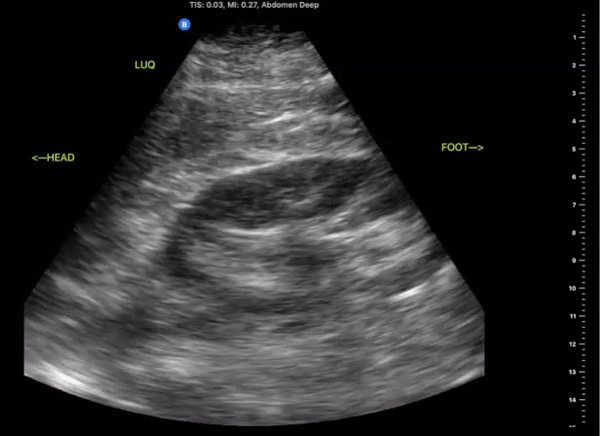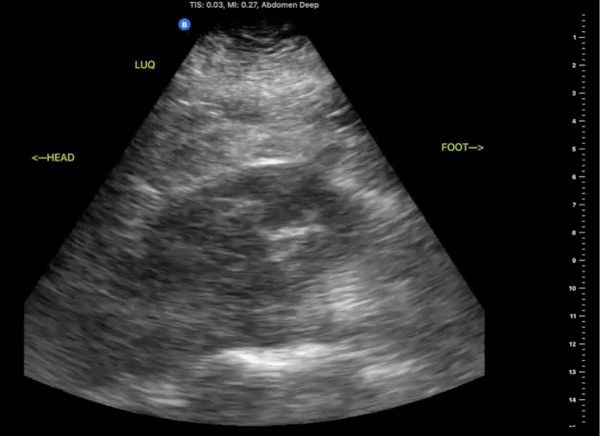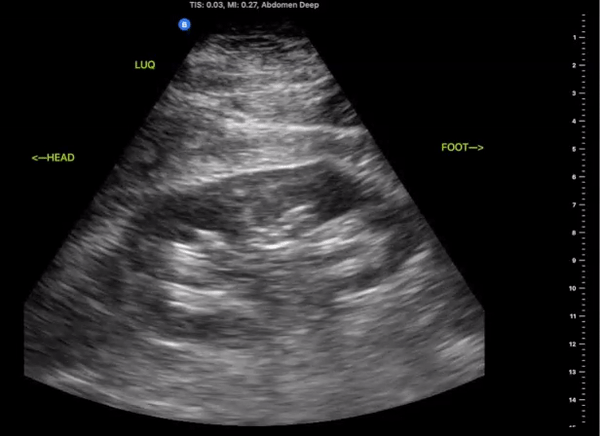
Left Upper Quadrant
(LUQ)
Probe/Preset:
Curvilinear, Phased Array/ FAST, Abdominal
Body Plane:
Coronal
Probe Indicator:
Towards Head
Depth:
At least 15cm
Location:
Posterior Axillary line the level of the xiphoid
Identify:
-
Left Kidney
-
Diaphragm
-
Spleen
Notes:
Scan through the area assessing the around the spleen, splenorenal space, and inferior pole of the kidney
_edited.jpg)

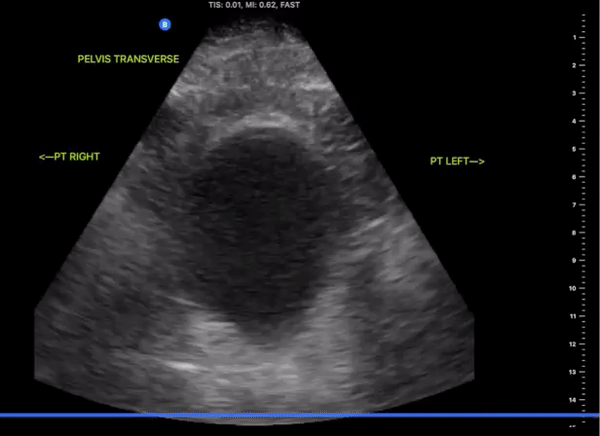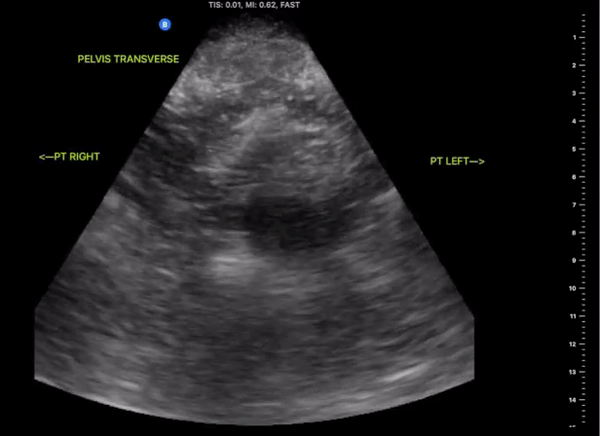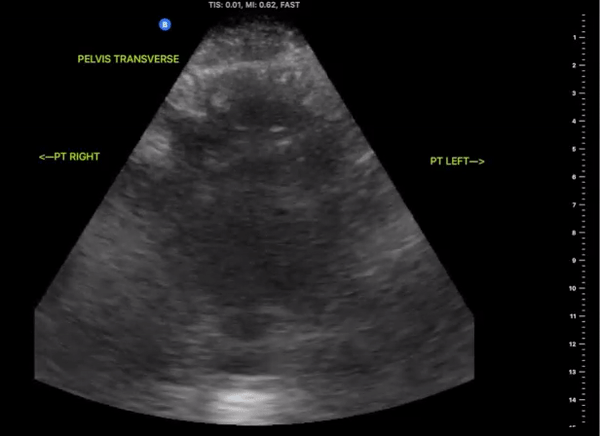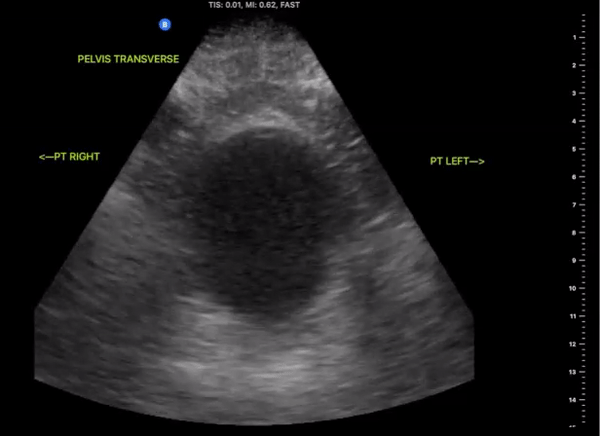
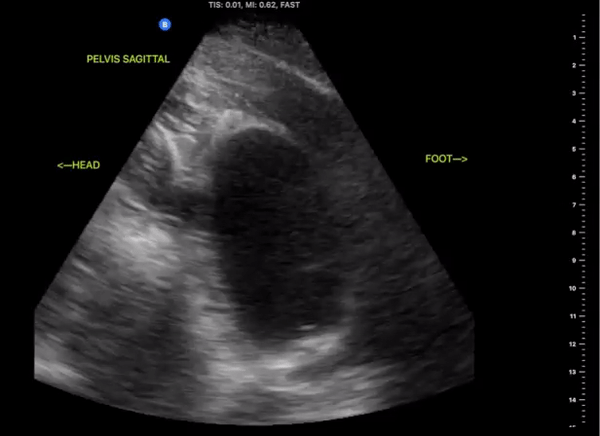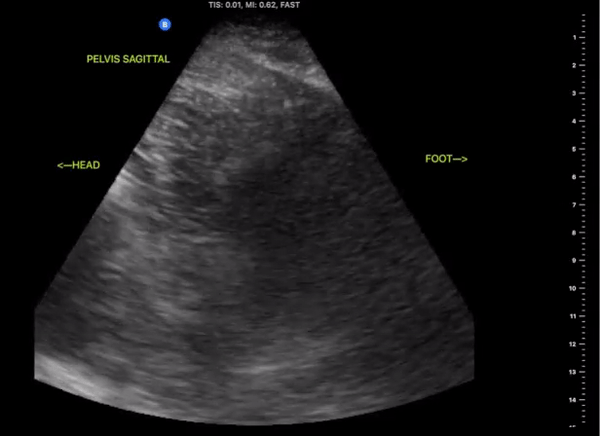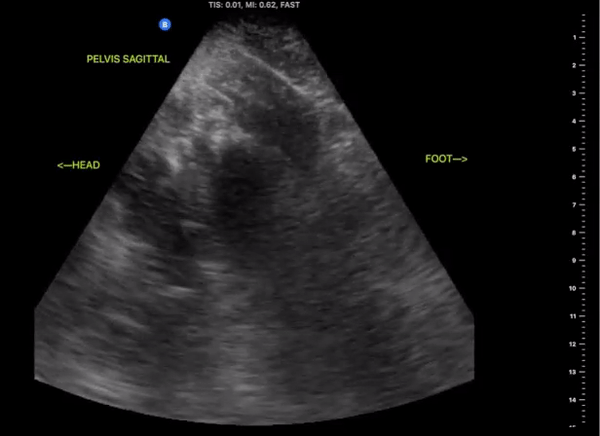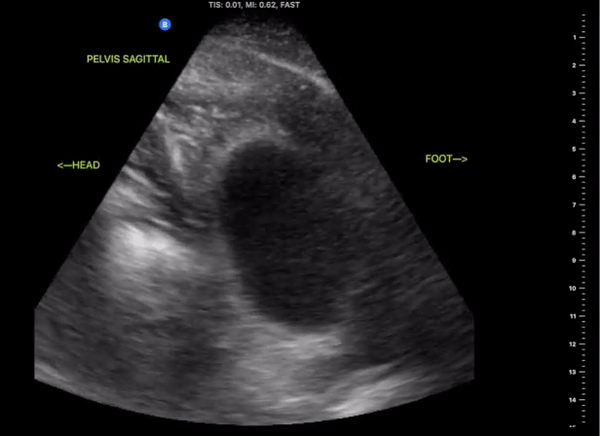
Pelvic Views
Probe/Preset:
Curvilinear / FAST, Abdominal, Bladder
Body Plane:
Transverse and Sagittal
Probe Indicator:
-
Transverse: Towards Patient’s Right
-
Sagittal: Towards Head
Depth:
At least 15cm
Location:
Patient Midline Superior to the pubic symphysis
Identify:
-
Bladder
-
Prostate (male)
-
Uterus/Uterine Stripe (female)
Notes:
Scan through the entire area assessing for the presents of free fluid. The bladder may be difficult to visualize if empty of urine. Small amounts of free fluid in pregnant females are a normal variant.
_edited.jpg)